Core Research Areas
The SIMSIS Laboratory envisions advancing the science and practice of physical infrastructure Digital Twins (DTs) by synthesizing the Digitization, Virtualization & Cognition, and Human-DT Interaction into a unified development workflow. Through their synthesis and practical applications, the Laboratory aims to enhance the resilience, reliability, and adaptive management of infrastructure systems, spanning both individual assets and interconnected networks.
To achieve this vision, the SIMSIS Laboratory focuses on the areas (below) in DT development and application at different modeling resolutions with strong emphasis on their Verification, Validation, and Uncertainty Quantification (VVUQ), including their collective impact on decision-making, and infrastructure resilience and reliability, with the goal of translating the DT development advancements into practical, real-world applications:
1) Digitization
Digitization develops scalable, continuous infrastructure sensing strategies, ranging from human-based inspections to robotic and urban data sources, to transform physical infrastructure into structured digital formats for real-time monitoring and DT model updates.
2) Virtualization & Cognition
This area combines realistic 3D modeling, simulation, and intelligent behavioral modeling, enhanced by AI, data and physics-driven methods, data assimilation, model updating, and immersive visualization, to enable "living", interpretable, and predictive digital twins of infrastructure.
3) Human–DT Interaction
This area investigates how immersive, collaborative environments and natural language interfaces support intuitive, informed human decision-making that completes the feedback loop between DT insights and real-world actions.
4) Multi-Scale DT Architecture
This research develops hierarchical, resolution-aware DT frameworks that integrate models across scales with needed LoDs, balancing fidelity, performance, and data needs, to enable scalable assessment and coordination from elements to infrastructure networks.
5) Application for Resilience and Reliability
This area evaluates how DT-informed strategies measurably improve infrastructure resilience and reliability under both normal operations and extreme conditions, using scenario simulations and performance metrics to guide practical impact.
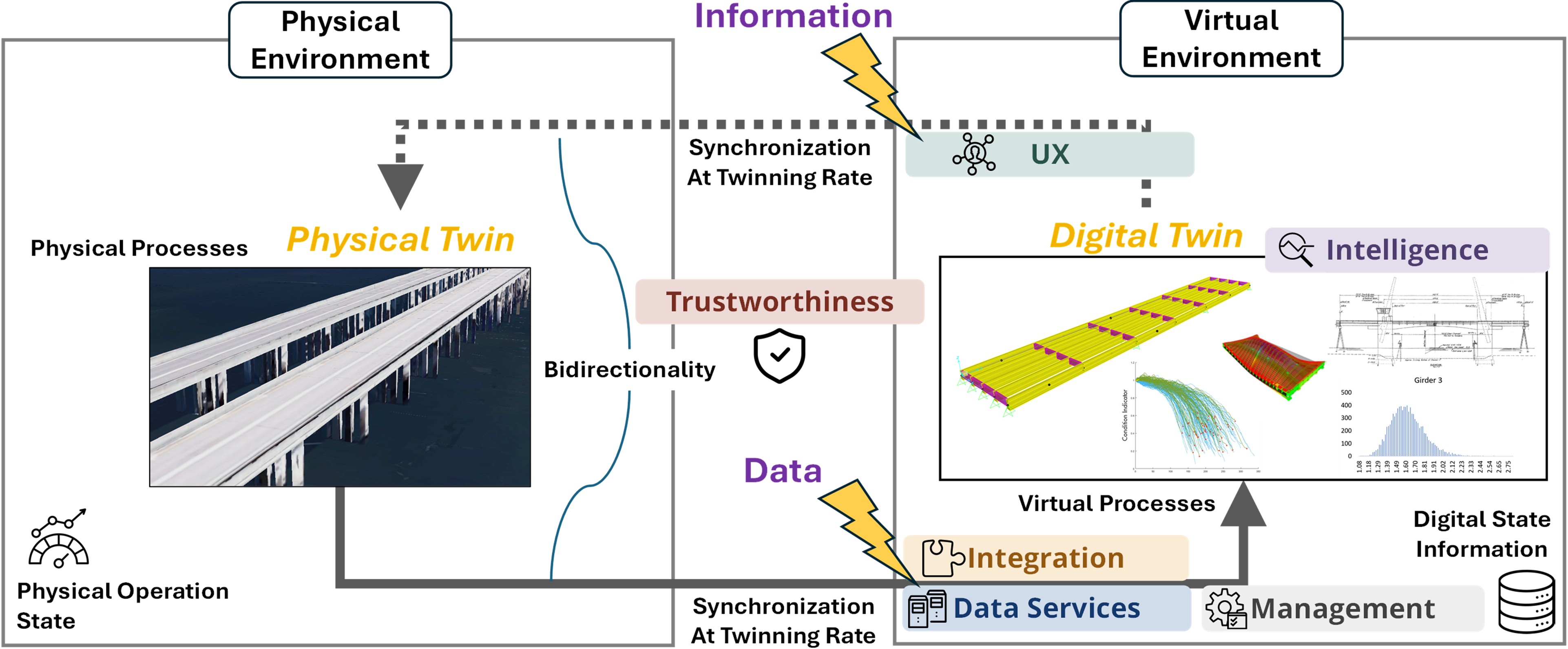
The Laboratory further engages with broader and emerging domains and capabilities of DT development, including data and model management, as well as trustworthiness. These additional capabilities align with the DT Capabilities Periodic Table (CPT), developed by the Digital Twin Consortium (DTC). This global industry consortium establishes the practices and standards for DT systems. The CPT’s latest release (Version 1.2) as shown in Figure 1 provides a comprehensive, vendor-agnostic framework for organizing the functional capabilities required to design, implement, and sustain scalable and trustworthy DTs.
Figure 1. DT capabilities periodic table v1.2 by Digital Twin Consortium.
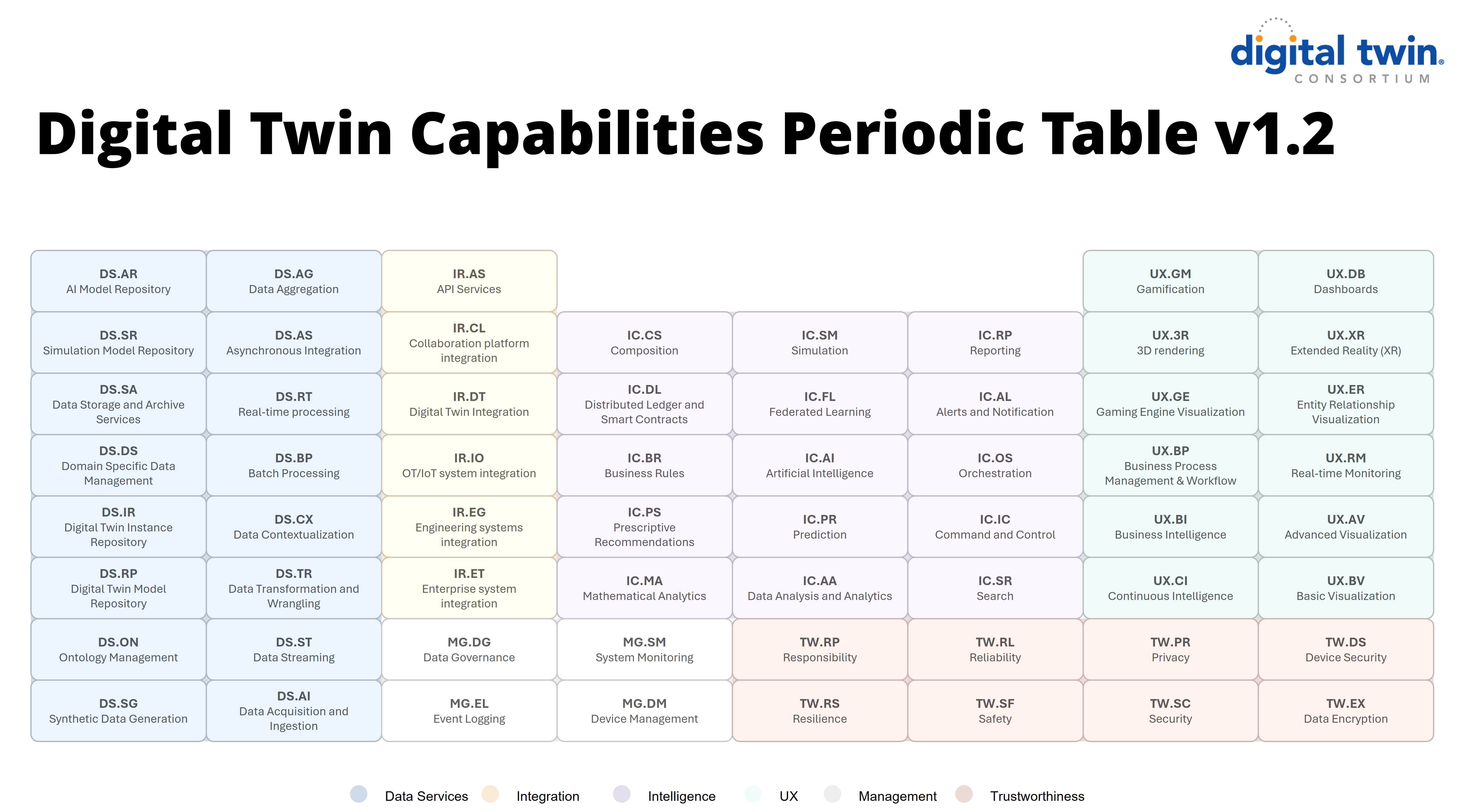
In terms of applying DTC’s DT capabilities in real-world contexts, Figure 2 illustrates the operation of a bridge DT, showcasing the interaction between the physical and digital counterparts within their respective environments. This diagram example illustrates how integrated sensing, modeling, and visualization workflows, facilitated by DT capabilities, can support dynamic condition assessment, operational monitoring, and informed decision-making throughout the infrastructure lifecycle.
Figure 2. physical infrastructure DT capabilities in an example application.